
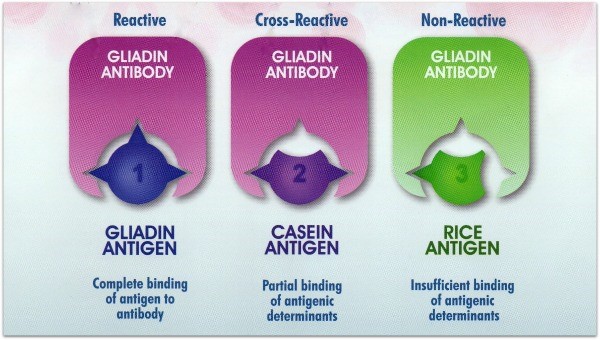
These tests make use of the cross-reactivity of antibodies. In clinical diagnosis, heterophile antibody tests are used to rapidly detect antibodies generated against the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis. Reaction can confirm that whether the ELISA kit is specific for detecting a certain protein of interest. The cross-reaction acrossĭifferent species can be used to explain certain immunopathological phenomena, diagnose certain infectious diseases, or induce immune responses against antigens that are difficult to prepare. Many human antigen-derived antibodies show significant cross-reactivity with the homologous proteins in non-human organisms, such as mouse, rat, and rabbit. For example, the cross-reactivity of an antibody enables it to detect the homologous proteins in multiple model Ĭross-reactivity can improve the utility of an antibody. The antibody reacts to another compound possessing a chemical structure similar to the targeted drug. A cross-reaction may lead to a false positive interference in drugs of abuse screening tests because In serological diagnosis, cross-reactivity of antibodies will cause confusion in specific diagnosis or identification.īesides, cross-reactivity can interfere with the results of immunoassays and affect reproducibility. The induction or exacerbation of infective diseases, autoimmune diseases, and allergy as a consequence of inappropriate or deleterious inflammatory responses related to host tissue destruction. Offensive roles of antibody cross-reactivity are mainly reflected in However, antibody cross-reactivity may be detrimental for the hosts. Evidence has been shown that the antibody cross-reactivity is a mechanism to escape the immune response for numerous human pathogens, including schistosomiasis, influenza In other words, the defensive action of antibody cross-reactivity imparts a broader immunity against pathogens or provides cross-protective immunity to related The cross-reactive antibody provides cross-protective immunity to related pathogen strains orĪntigenic variants in natural epidemiology. The Biological Significance of Cross-reactivityĬross-reactivity of antibodies shows both defensive and offensive properties. To some extent, cross-reactivity greatly reduces specificity.ģ. While cross-reactivity assesses the degree to which different antigens resemble the immune Specificity evaluates the extent to which the immune system distinguishes between different antigens. In immunoassays, cross-reactivity ofĪntibody (polyclonal antibody) enhances the sensitivity of the result and allows for the detection of antigens with low abundance. It is the most prominent feature of immune response and is the basic basis for the prevention and diagnosis inĬross-reactivity refers to a situation in which an antibody recognizes and binds to two or more antigens that are highly homologous or possess the same epitope. The specificityĮnables to precisely detect a target antigen thus avoiding measurement of impostor antigens. The specificity is determined by the types, arrangement order, and spatial configuration of epitope(s) on the antigen. Noted that this unique epitope may be present on more than one antigen. In immunology, specificity refers to the ability of paratopes on an antibody to recognize and interact with only a single epitope on the corresponding antigen. The Association and Difference between Cross-Reactivity and Specificity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
